Diagnosing Obesity
Obesity remains underdiagnosed and undertreated.2
Only 55% of people with obesity reported receiving a formal diagnosis, and even fewer received follow-up obesity care2
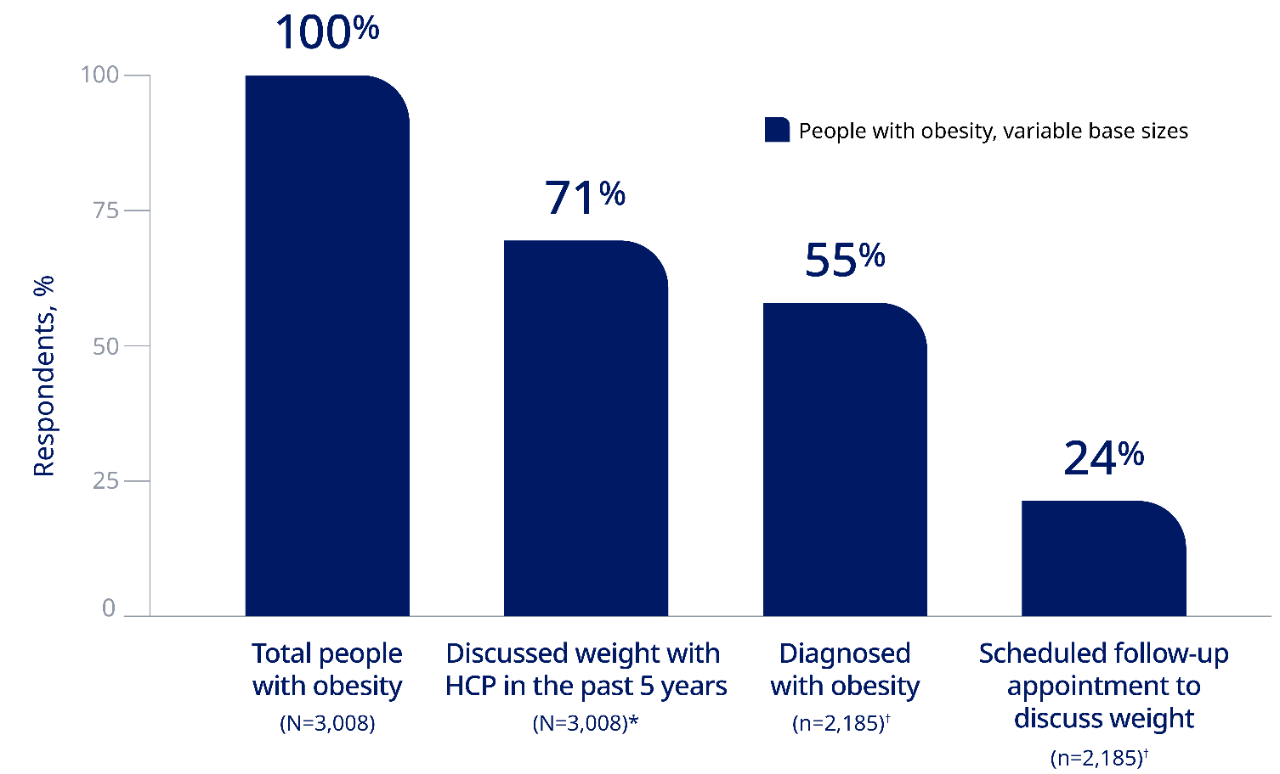
*Either “discussed being overweight” (68%) or “discussed losing weight” (64%) with their health care professional.2
†Among the 71% who have had a conversation with their health care professional about obesity in the past 5 years.2
An observational study of more than 688,000 patients showed that a formal diagnosis of obesity can help address stigma and weight bias and is associated with better outcomes.3
Diagnose your patients with obesity using the following protocols recommended by AACE/ACE4
Evaluation
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Clinical laboratory
- Review of systems, emphasizing obesity-related complications
- Obesity history
- Graph weight vs age
- Lifestyle patterns and preferences
- Previous interventions
Anthropometric diagnosis
- Confirm that elevated BMI represents excess adiposity
- Measure waist circumference to evaluate cardiometabolic disease risk
Clinical diagnosis
- Normal weight: BMI <25 kg/m2 or <23 kg/m2 in certain ethnicities with waist circumference below regional/ethnic cutoffs‡
- Overweight: BMI 25 kg/m2–29.9 kg/m2
- Obesity: BMI ≥30 kg/m2
- Evaluate checklist of obesity-related complications

DIAGNOSING
AACE/ACE guidelines
These guidelines, established by endocrinologists, provide a frame of reference for managing obesity.
Reframing Obesity Management
Dr. Holly Lofton discusses how obesity is often managed differently than other chronic diseases and highlights the need for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Video length: 4:41
Patient Profiles

Patient with obesity and OA
Lance
Lance continues to have knee pain despite adopting new healthy habits of getting active and eating healthier foods.

Patient with obesity and PCOS
Maria
Maria gained weight after pregnancy and noticed changes in her cycles.

Patient with obesity and CVD risk
Simone
Simone has struggled with weight for most of her life. Now, it may be putting her at risk for CVD.
AACE, American Association of Clinical Endocrinology; ACE, American College of Endocrinology; BMI, body mass index; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HCP, health care professional; OA, osteoarthritis; PCOS, polycystic ovary syndrome.
1. Glauser TA, Roepke N, Stevenin B, Dubois AM, Mi Ahn S. Physician knowledge about and perceptions of obesity management. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2015;9(6):573-583.
2. Kaplan LM, Golden A, Jinnett K, et al. Perceptions of barriers to effective obesity care: results from the National ACTION Study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2018;26(1):61-69.
3. Ciemins EL, Joshi V, Cuddeback JK, Kushner RF, Horn DB, Garvey WT. Diagnosing obesity as a first step to weight loss: an observational study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2020;28(12):2305-2309.
4. Garvey WT, Mechanick JI, Brett EM, et al; Reviewers of the AACE/ACE Obesity Clinical Practice Guidelines. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for medical care of patients with obesity. Endocr Pract. 2016;22(suppl 3):1-203.










