Start the Conversation
There are several ways to start the conversation about long-term weight management
Supporting your patients to achieve weight loss of ≥5% can have a clinically meaningful impact on some comorbidities.2
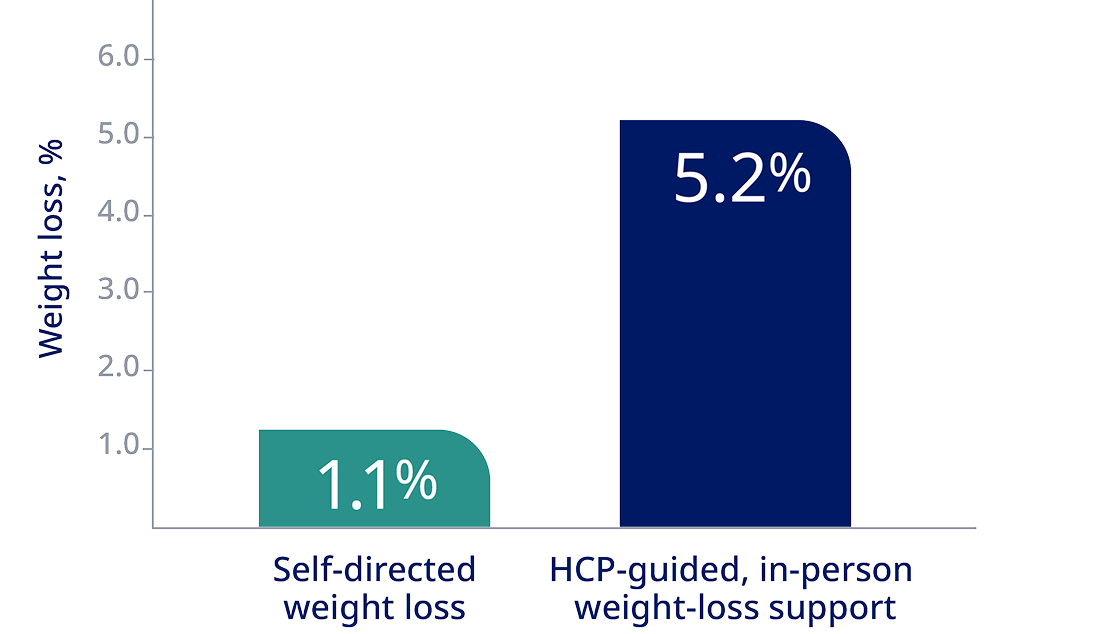
Adult patients with obesity lost more weight with HCP counseling than with a self-directed program3*
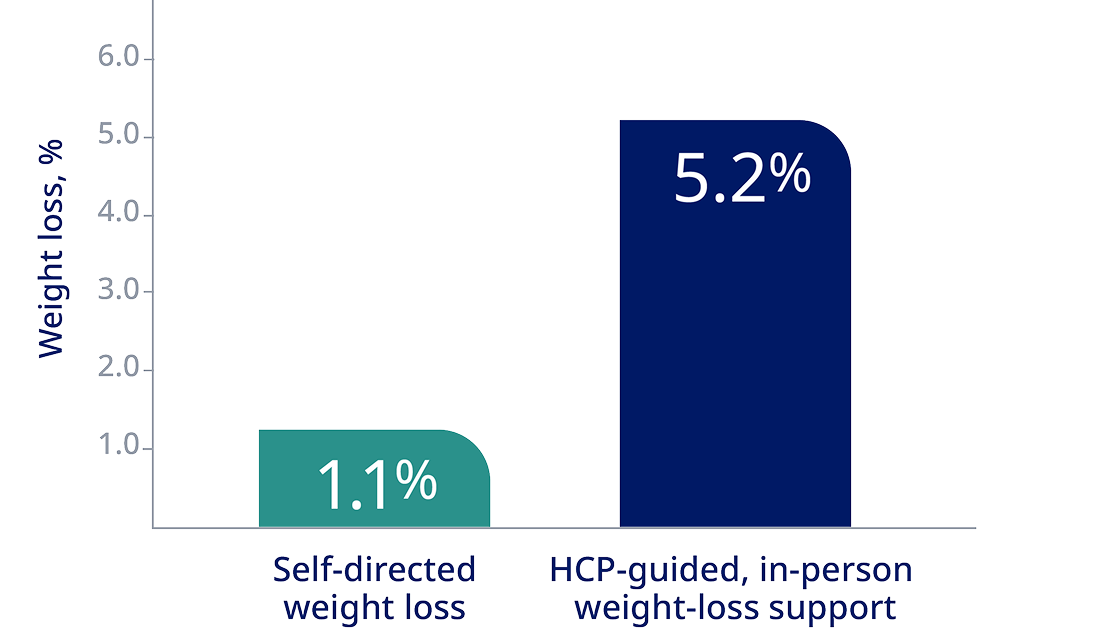
*A randomized, controlled trial involving 415 patients with obesity with at least one cardiovascular risk factor evaluated the effects of 2 behavioral weight-loss interventions over 24 months. The study found that patients receiving either remote support (5.0% weight loss) or in-person support (5.2% weight loss) achieved significantly greater weight loss compared with those in a self-directed program (1.1% weight loss). At 24 months, the mean change in weight from baseline was -0.8 kg in the control group, -4.6 kg in the group receiving remote support only, and -5.1 kg in the group receiving in-person support.3
Patient efforts improved after weight-loss discussions with their HCPs
In one study, patients were4†:
63
%
more likely to attempt to lose weight
67
%
more likely to attempt to change their diet
58
%
more likely to attempt to change their exercise patterns
†Results from surveys and audio-recorded preventative health care and chronic care visits between 25 female patients with overweight or obesity and their HCPs. The study recorded their conversations for quantity and quality of weight-related discussions to assess the correlation between HCP weight-loss discussions and patient motivation to lose weight, change their diet, or change their lifestyle patterns.4

“We need to see ourselves as partners with our patients, to give them the time, attention, and support they need throughout their weight-management journey.”
Carlos Campos, MD
Primary Care Physician, Board-Certified Obesity Specialist

‡Prevalence of obesity based on NHANES data for 2021-2023 and data from the 2024 US Census estimates.
Start with a framework that supports dialog and behavior change
The 5As model is a behavioral intervention strategy that’s been modified for obesity management. It helps increase patient motivation and behavioral change in weight-management consultations.8
ASK
for permission to discuss weight and explore readiness to change8
ASSESS
obesity class and stage, and any barriers8
ADVISE
on obesity risks and explain benefits8
AGREE
on realistic weight-loss expectations with a focus on behavioral goals8
ASSIST
by providing education, resources, and support8
Be aware of weight bias and how it can affect your patients with obesity and your practice
Because perceived weight bias among health care professionals can impact health care utilization by people with obesity, interventions to reduce explicit weight bias are critical. These include:
- A formal diagnosis, which has been associated with better outcomes for patients with obesity9
- Education that emphasizes the complex causes of obesity has been shown to reduce weight bias in the health care setting10
- Training and practice in patient-centered communication strategies can reduce the impact of bias on the quality of communication10
Approach obesity care with compassion
See, acknowledge, and treat the whole person
Patients with obesity often feel that their physicians are stigmatizing their weight. By focusing on the patient’s weight and health, you can help them develop sustainable lifestyle habits. This holistic approach involves considering their emotional, physical, nutritional, social, and spiritual health.11
Identify bias and assumptions
Patients who have experienced bias may have developed consequences such as unhealthy eating behaviors and distrust of health care professionals, but this can be overcome with careful consideration of your communication style.11
Practice patient-centered communication
Consider motivational interviewing techniques, in which you emphasize your patient’s autonomy through empathy and reflective listening.11
Create a welcoming environment
This can include everything from appropriately sized furniture and equipment to weighing patients in private. It’s also useful to give your staff opportunities for sensitivity training focused on obesity.11
Pursue lifelong learning
Take advantage of the educational resources offered by organizations such as the American Board of Obesity Medicine and the Obesity Action Coalition to ensure you stay ahead of the curve.11
1. Camacho S, Ruppel A. Is the calorie concept a real solution to the obesity epidemic? Glob Health Action. 2017;10(1):1289650.
2. Ryan DH, Yockey SR. Weight loss and improvement in comorbidity: differences at 5%, 10%, 15%, and over. Curr Obes Rep. 2017;6(2):187-194.
3. Appel LJ, Clark JM, Yeh JC, et al. Comparative effectiveness of weight-loss interventions in clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(21):1959-1968.
4. Pollak KI, Østbye T, Alexander SC, et al. Empathy goes a long way in weight loss discussions. J Fam Pract. 2007;56(12):1031-1036.
5. Emmerich SD, Fryar CD, Stierman B, Ogden CL. Obesity and severe obesity prevalence in adults: United States, August 2021-August 2023. NCHS Data Brief. 2024;(506):1-10.
6. US Census. Quick facts. Accessed June 11, 2025. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/LND110210
7. Spahlholz J, Baer N, Konig H-H, Riedel-Heller SG, Luck-Sikorski C. Obesity and discrimination – a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Obes Rev. 2016;17(1):43-55
8. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Five Major Steps to Intervention (The “5 A’s”). Accessed June 11, 2025. https://www.ahrq.gov/prevention/guidelines/tobacco/5steps.html
9. Ciemins EL, Joshi V, Cuddeback JK, Kushner RF, Horn DB, Garvey WT. Diagnosing obesity as a first step to weight loss: an observational study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2020;28:2305-2309.
10. Puhl RM, Phelan SM, Nadglowski J, Kyle TK. Overcoming weight bias in the management of patients with diabetes and obesity. Clin Diabetes. 2016;34(1):44-50.
11. Kennedy AB, Taylor SS, Lavie CJ, Blair SN. Ending the stigma: improving care for patients who are overweight or obese. Fam Pract Manag. 2022;29(2):21-25.