In a study measuring 10-year weight gain in over 13,000 adults in the United States, the mean weight gain was approximately 4.2 kg, or 8.8 lb.8*
obesity as a disease
Obesity is a serious, chronic, and progressive condition that can require long-term medical management4,5
The prevalence of obesity has steadily increased in recent decades5
The age-adjusted prevalence of obesity has increased from 30.5% to more than 40% since 19996,7
Trends in age-adjusted obesity and severe obesity prevalence among adults aged 20 years and older, United States 1999-2000 through 2021-2023*
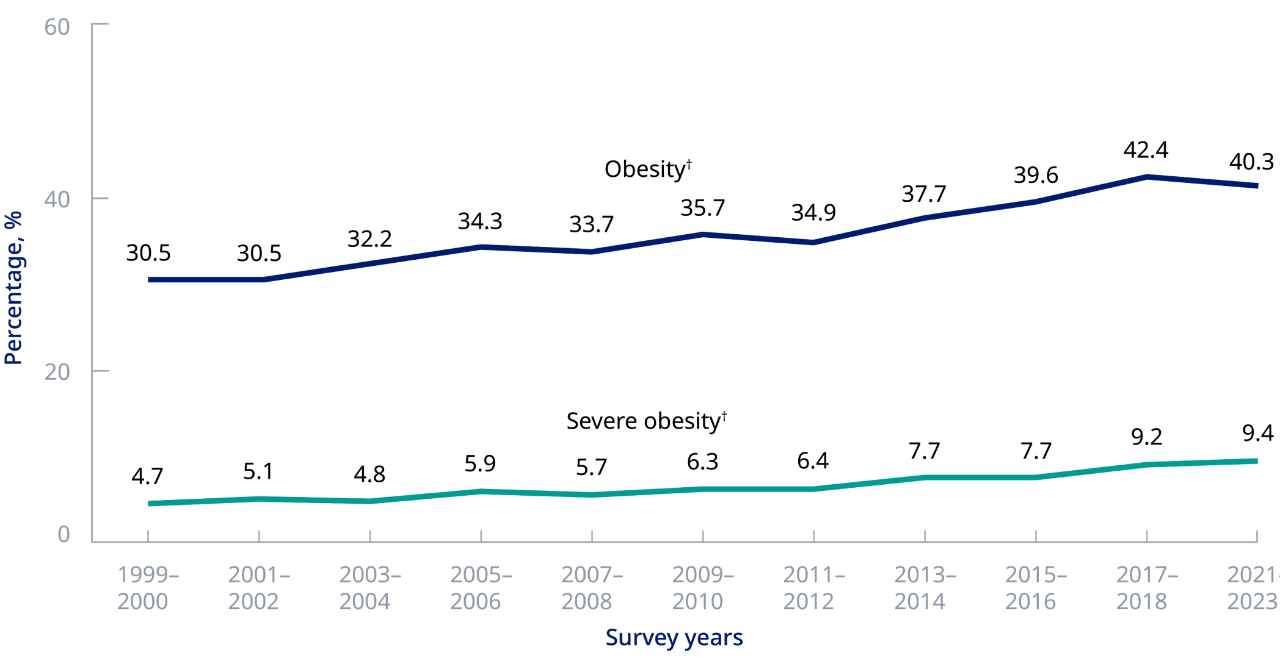
*Estimates were age-adjusted by the direct method to the 2000 US census population, using the age groups 20-39, 40-59, and 60 years and over.
†Significant linear trend. Based on NHANES 2015-2023 data; CVD comprising CHD, HF, stroke, and hypertension in adults ≥20 years of age.
Data from 2019-2020 is not included as NHANES suspended data collection due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
CHD, congestive heart failure; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HF, heart failure; NHANES, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
Sustaining weight loss can be difficult.
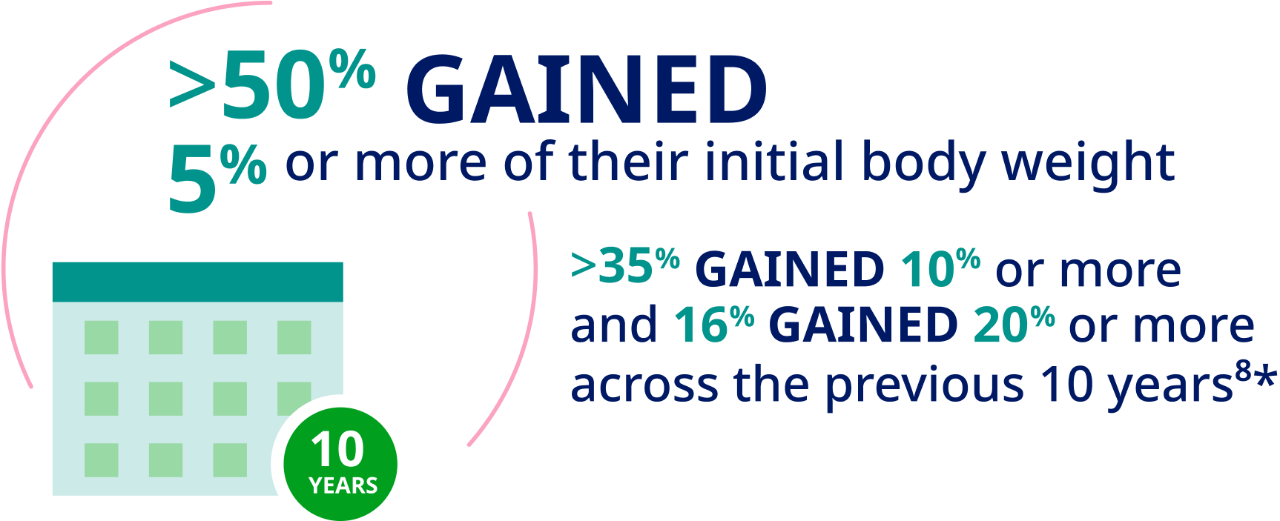
*Cross-sectional data collected from 2011-2018, delimited to adults 36-79 years of age; current body weight was measured, and weight 10 years earlier was reported by participants.8
After weight loss from caloric restriction, natural processes can change appetite-regulating hormones, leading to a tug-of-war between weight loss and weight regain. This may cause obesity to progress, leading to other weight and health complications.5,9,10
The number of adults in the United States living with obesity approaches the number of adults living with hypertension and/or CVD7,11-14

‡Prevalence of obesity based on NHANES data for 2013-2023 and data from the 2024 US census estimates.8,14
§Based on NHANES 2015-2018 data; CVD comprising CHD, HF, stroke, and hypertension in adults ≥20 years of age.
‖Approximately 101M of these have hypertension.

“A number of health care professionals still believe obesity is a lifestyle choice…obesity is a chronic disease that should be approached with the same sentiment as other chronic conditions.”
Carlos Campos, MD
Primary Care Physician, Board-Certified Obesity Specialist
Factors contributing to obesity can be classified as internal and external15-19
Internal factors include:

Genetics15
Certain genes can affect appetite regulation, energy expenditure, and fat storage.
External factors include:

Technology16
Modern-day advances in technology may have contributed to the obesity epidemic by increasing food intake and sedentary behavior.

Cultural17
Biology, psychology, and economics reflect culture and the circumstances in which we eat, the type and quantity of what we eat, and with whom we eat.

Economic18
Across income groups, direct costs of obesity and overweight (25 kg/m2–29.9 kg/m2) account for up to 38.2% of total cost in high-income countries, while indirect costs can account for as much as 88.6% of total costs in lower- and middle-income countries.¶
¶The study employed a cost-of-illness approach to estimate the economic impacts of overweight and obesity (OAO) from a societal perspective. Data were sourced from published studies and global databases, covering direct and indirect costs of OAO between 2019 and 2060 across 161 countries. The analysis included country-specific data on OAO prevalence, health care expenditure, wage rates, gross domestic product, and employment rates, among other parameters.18
Societal19
Higher rates of obesity have been linked to a variety of social adversities, including poverty, low socioeconomic status, food insecurity, malnourishment, and consumption of nutrient-poor diets based on affordability.
Words Matter in the Obesity Conversation
Dr. Sobel shares how the way you speak about obesity can affect your patients.

1. Kaplan LM, Golden A, Jinnett K, et al. Perceptions of barriers to effective obesity care: results from the National ACTION Study. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2018;26(1):61-69.
2. English S, Vallis M. Moving beyond eat less, move more using willpower: reframing obesity as a chronic disease impact of the 2020 Canadian obesity guidelines reframed narrative on perceptions of self and the patient-provider relationship. Clin Obes. 2023;13(6):e12615.
3. Tondt J, Freshwater M, Hurtado Andrade M, et al. Obesity algorithm 2024. Obesity Medicine Association. January 2024. Accessed June 11, 2025. https://obesitymedicine.org/resources/obesity-algorithm/
4. Bray GA, Kim KK, Wilding JPH; World Obesity Federation. Obesity: a chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes Rev. 2017;18(7):715-723.
5.. Garvey WT, Mechanick JI, Brett EM, et al; Reviewers of the AACE/ACE Obesity Clinical Practice Guidelines. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for medical care of patients with obesity. Endocr Pract. 2016;22(suppl 3):1-203.
6. Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief. 2020;(360):1-8.
7. Emmerich SD, Fryar CD, Stierman B, Ogden CL. Obesity and severe obesity prevalence in adults: United States, August 2021-August 2023. NCHS Data Brief. 2024;(506):1-10.
8. Tucker LA, Parker K. 10-year weight gain in 13,802 US adults: the role of age, sex and race. Journal of Obesity. 2022;(7652408):1-10.
9. Lam YY, Ravussin E. Analysis of energy metabolism in humans: a review of methodologies. Mol Metab. 2016;5(11):1057-1071.
10. Sumithran P, Prendergast LA, Delbridge E, et al. Long-term persistence of hormonal adaptations to weight loss. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(17):1597-1604.
11. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Adult obesity facts. Published May 14, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult-obesity-facts/index.html
12. Chobufo MD, Gayam V, Soluny J, et al. Prevalence and control rates of hypertension in the USA: 2017-2018. Int J Cardiol Hypertens. 2020;6:100044.
13. Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(8):e254-e743.
14. US Census. Quick facts. Accessed June 11, 2025. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/LND110210
15. Mahmoud R, Kimonis V, Butler MG. Genetics of obesity in humans: a clinical review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11005.
16. Gilmore LA, Duhé AF, Frost EA, Redman LM. The technology boom: a new era in obesity management. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2014;8(3):596-608.
17. Masood M, Aggarwal A, Reidpath DD. Effect of national culture on BMI: a multilevel analysis of 53 countries. BMC Public Health. 2019;19:1212.
18. Okunogbe A, Nugent R, Spencer G, Ralston J, Wilding J. Economic impacts of overweight and obesity: current and future estimates for eight countries. BMJ Glob Health. 2021;6(10):e006351.
19. Hemmingsson E, Nowicka P, Ulijaszek S, Sørensen TIA. The social origins of obesity within and across generations. Obes Rev. 2023;24(1):e13514.




